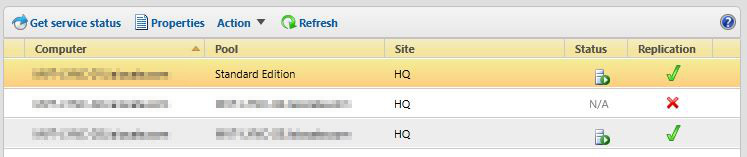
Recently I came across an issue where the Edge server would not replicate the topology. After spending some time looking through firewall ACLs, NAT exemptions, packet captures and the rest of the usual networking stuff, it turns out the problem was WAY more obscure than simple connectivity…

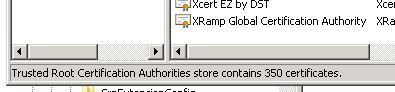
If your Edge server’s Trusted Root CA store contains over 100 entries, the SChannel security package will truncate this list internally and depending on where your internal Root CA sits in the alphabetical order, it could be truncated and affect the ability to replicate the Lync topology over HTTPS 4443.

To resolve this issue, there are two options:
1. Delete unnecessary certificates from the Trusted Root CA store of the Edge server. This could potentially affect federated partners depending on which Root CAs you delete, but is a quick and easy way to fix the problem.
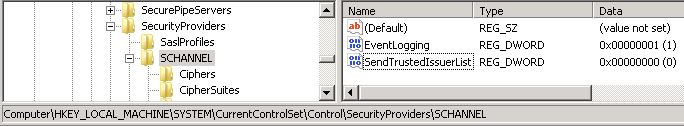
2. Edit the registry on the Edge server to add a DWORD value, SendTrustedIssuerList, to the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL key and assign it a value of 0. This will prevent schannell.dll from truncating the Root CA list from the edge server, and allow validation tests to pass.

This was taken from the Technet’s Lync Forums here